Dental Implants and Gum Disease: Understanding the Connection
In today's world, maintaining oral health is paramount, particularly as we face challenges like gum disease and tooth loss. For many patients, the solution to these issues comes in the form of dental implants. This article aims to explore the vital connection between dental implants and gum disease, detailing how each influences the other and what you can do to ensure your smile remains healthy and vibrant.
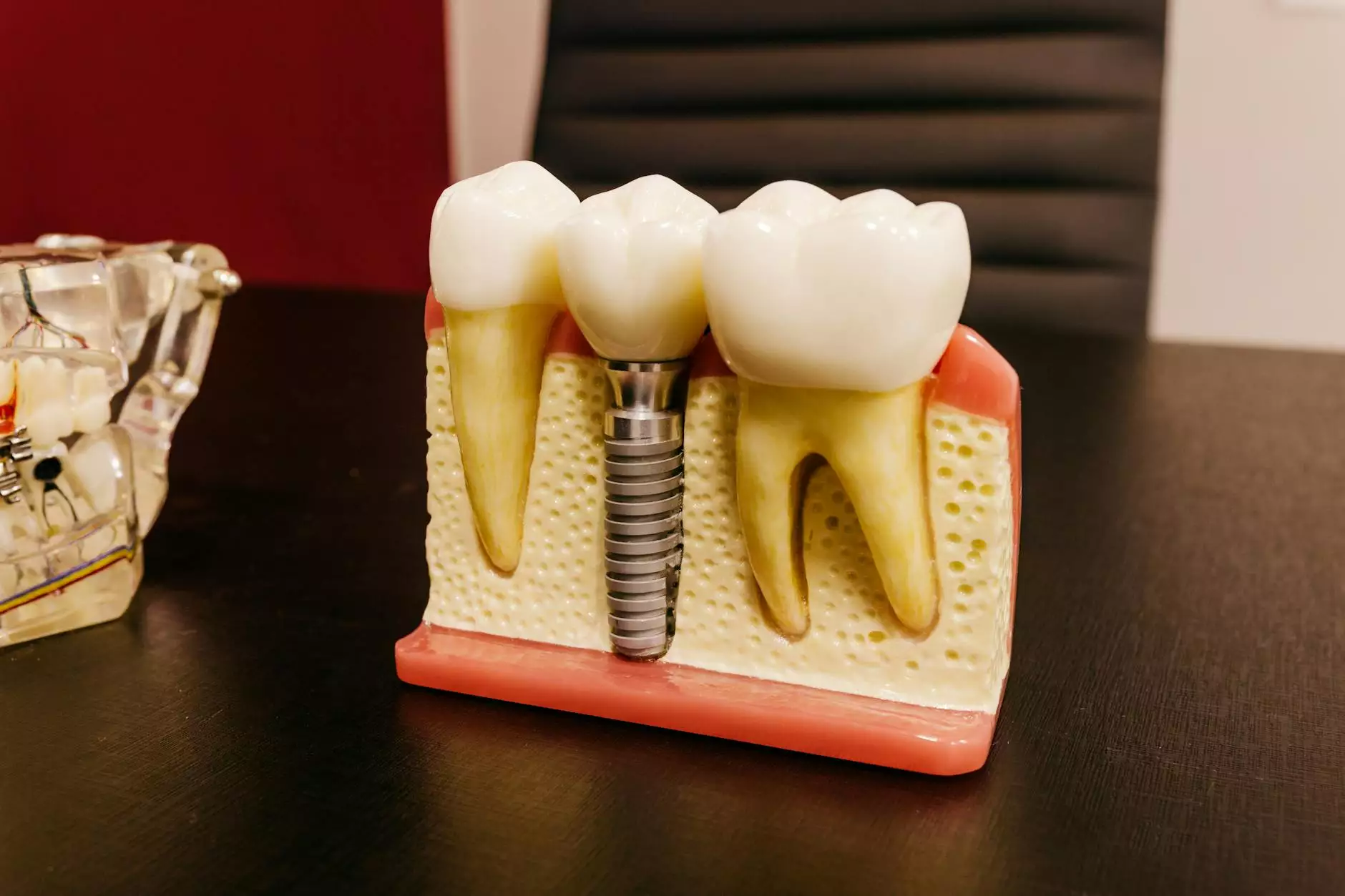
What are Dental Implants?
Dental implants are artificial tooth roots, usually made of titanium, that are surgically placed into the jawbone. They serve as stable foundations for replacement teeth or bridges. The advantages of dental implants over other tooth replacement options include:
- Durability: With proper care, implants can last a lifetime.
- Natural Appearance: Implants look and feel like natural teeth.
- Bone Preservation: They stimulate the jawbone, preventing bone loss.
- Improved Oral Health: They do not require the alteration of adjacent teeth.
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is an infection of the gums caused by plaque buildup on the teeth. It can lead to inflammation and, if untreated, can result in tooth loss. There are two primary stages of gum disease:
- Gingivitis: The early stage, where gums may become swollen and bleed, especially during brushing.
- Periodontitis: Advanced stage that can lead to tooth mobility and loss due to damage to the bone and connective tissue.
The Relationship Between Dental Implants and Gum Disease
Understanding the connection between dental implants and gum disease is crucial for those considering implants or those who already have them. Here's how they are intertwined:
1. Risk of Gum Disease Post-Implant Procedure
After receiving dental implants, it is essential to maintain good oral hygiene to prevent gum disease. Implants can be susceptible to peri-implantitis, an inflammatory condition similar to gum disease that affects the tissues surrounding the implant. Factors contributing to this include:
- Improper oral hygiene practices.
- Smoking, which impairs healing.
- Existing diabetes or other health issues.
2. Prevention Strategies
Preventing gum disease post-implant is critical. Here are several strategies to help:
- Regular Dental Visits: Schedule check-ups every six months for professional cleanings.
- Brushing and Flossing: Brush at least twice a day and floss daily, especially around the implant area.
- Antibacterial Rinses: Use a prescribed mouthwash to reduce bacteria.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintain a balanced diet and avoid tobacco products.
3. Symptoms to Watch For
Being aware of the symptoms of gum disease is vital for individuals with dental implants. Signs of potential issues include:
- Persistent bad breath.
- Swollen or bleeding gums.
- Pain around the implant site.
- Mobility of the implant.
Treating Gum Disease Associated with Dental Implants
If you find yourself facing gum disease after getting dental implants, early intervention is essential. Treatment options include:
1. Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing)
This non-surgical procedure removes tartar and plaque from below the gumline, helping to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
2. Antibiotics
Topical or systemic antibiotics may be prescribed to combat infection and assist in the healing process.
3. Surgery
In advanced cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to restore health to the gums around the dental implant. This may include:
- Flap surgery to reduce pocket depth.
- Bone grafts to strengthen the jawbone.
Long-term Care for Dental Implants
To ensure the longevity of your dental implants, it’s crucial to adopt a long-term care regimen that includes:
- Consistent Oral Hygiene: Stick to a meticulous daily routine of brushing and flossing.
- Regular Check-ups: Frequent evaluations with your dentist help to catch any signs of gum disease early.
- Nutritional Support: A diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports gum health.
Conclusion
The connection between dental implants and gum disease is increasingly recognized as a vital aspect of modern dentistry. Understanding the risks, preventive measures, and treatment options can lead to a successful outcome for anyone who has undergone implant surgery. Maintaining dedicated oral hygiene and being proactive about dental health can ensure that your dental implants remain a lasting solution rather than a momentary fix.
Your smile is worth it! For more information on ensuring the longevity of your dental implants or to discuss any concerns related to gum disease, please contact our team at 92 Dental.